【NLP】常规赛:中文新闻文本标题分类

该项目针对中文新闻文本标题分类任务,采用embedding+GRU+MLP模型,精度约0.8。先预处理数据,用Jieba分词,构建语料库和词向量映射,依标题长度分布设最大输入长度20。再搭建网络,训练时验证精度超0.9但测试精度较低,存在过拟合,可尝试BERT提升精度,适合新手参考。

项目导言:
该项目是我在针对 AI studio 常规赛:中文新闻文本标题分类搭建的项目,目前精度在0.8左右。只简单的使用了embedding+GRU+MLP,但是项目是从头开始搭建的,并没有使用一些复杂的模型,并且项目带有很多解释说明,所以可供新手朋友参考。
(复杂的模型比如BERT,如果想提高精度,可以尝试使用该模型,模型的具体细节可以参考《BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding》)
项目思路
在看到这个项目之后,首先明确这是个分类任务,类似于手写数字识别这种,因此我们可以参照手写数字识别的思路处理该问题。
首先,对数据集进行预处理(包括去换行符,将标题与类别分离,创建项目语料库等等),然后将我们的输入进行向量化。在向量化过程中,我们使用了Python一个很正要的库:Jieba库。 它是优秀的中文分词第三方库,可以参考Jieba使用说明。然后使用Paddle框的数据集构建方法进行构建我们网络的输入。
然后,我们构建网络模型。对于手写数字识别网络,我们仅仅使用几层简单的全连接网络构建一个MLP多层感知机就可以获得比较好的结果,我们首先进行了这种尝试,结果不是很理想。然后鉴于这个是文本处理任务,我们使用了一个简单的循环神经网络(GRU,门控循环单元)和嵌入层来进行实验,在训练的时候取得不错的结果(val 精度超过0.9),但是在提交之后效果并不是很好(test精度在0.8左右),说明我们的模型存在过拟合,还可以进一步优化。
1.导入工具包
In [1]import paddleimport numpy as npimport jiebaimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom tqdm import tqdm登录后复制
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/__init__.py:107: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working from collections import MutableMapping/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/rcsetup.py:20: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working from collections import Iterable, Mapping/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/colors.py:53: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working from collections import Sized登录后复制
2.定义文件路径
In [2]train_data_path="data/data118554/train.txt"val_data_path='data/data118554/dev.txt'test_data_path='data/data118554/test.txt'登录后复制
3. 读取文件
In [3]def openfile(path): with open(path,'r',encoding='utf-8') as source: lines=source.readlines() return lines登录后复制 In [4]
train_lines=openfile(train_data_path)val_lines=openfile(val_data_path)test_lines=openfile(test_data_path)登录后复制
3.1 打印数据集,查看数据集内容及数目
每条数据集是由 “新闻标题文本+类别(标签)”构成,中间由空格隔开。
In [5]print(len(train_lines))print(train_lines[0])print(len(val_lines))print(val_lines[0])print(len(test_lines))print(test_lines[0])登录后复制
752471网易第三季度业绩低于分析师预期科技80000网民市民集体幻想中奖后如果你中了9000万怎么办cai票83599北京君太百货璀璨秋色 满100省353020元登录后复制
4. 数据预处理,包括去换行、分割、jieba分词
In [6]def data_process(datalines,test=False): datalist=[] labellist=[] for datas in datalines: #data,label=datas.strip().split() data=datas.strip().split() #print(data) if test==False: labellist.append(data[-1]) if len(data[:-1])>1: for i in range(1,len(data[:-1])): data[0]+=","+data[i] else: if len(data)>1: for i in range(1,len(data)): data[0]+=","+data[i] datalist.append(data[0]) return datalist,labellist登录后复制 In [7]
train_data,train_label=data_process(train_lines)val_data,val_label=data_process(val_lines)test_data,_=data_process(test_lines,test=True)登录后复制
4.1 打印经过简单处理(删除换行符,将标题和类别分开)
In [8]for i in range(5): print(train_data[i],' ',train_label[i])print("***********")for i in range(5): print(val_data[i],' ',val_label[i]) print("***********")for i in range(5): print(test_data[i])登录后复制 网易第三季度业绩低于分析师预期 科技巴萨1年前地狱重现这次却是天堂,再赴魔鬼客场必翻盘 体育美国称支持向朝鲜提供紧急人道主义援助 时政增资交银康联,交行夺参股险商首单 股票午盘:原材料板块领涨大盘 股票***********网民市民集体幻想中奖后如果你中了9000万怎么办 cai票PVC期货有望5月挂牌 财经午时三刻新作《幻神录―宿命情缘》 游戏欧司朗LLFY网络提供一站式照明解决方案 家居试探北京楼市向何方:排不完的队,涨不够的价 房产***********北京君太百货璀璨秋色,满100省353020元教育部:小学高年级将开始学习性知识专业级单反相机,佳能7D单机售价9280元星展银行起诉内地客户,银行强硬客户无奈脱离中国的实际,强压RMB大幅升值只能是梦想登录后复制
4.2 Jieba库的使用
In [9]def jieba_process(datalist): data=[] for datas in tqdm(datalist): data.append(jieba.lcut(datas)) return data登录后复制 In [10]
train_data=jieba_process(train_data)val_data=jieba_process(val_data)test_data=jieba_process(test_data)登录后复制
0%| | 0/752471 [00:00登录后复制4.3 查看分词结果
In [11]print(train_data[0],train_label[0])print(val_data[0],val_label[0])print(test_data[0])登录后复制['网易', '第三季度', '业绩', '低于', '分析师', '预期'] 科技['网民', '市民', '集体', '幻想', '中奖', '后', '如果', '你', '中', '了', '9000', '万', '怎么办'] cai票['北京', '君太', '百货', '璀璨', '秋色', ',', '满', '100', '省', '353020', '元']登录后复制5.从训练集中提取标签种类,并进行类别编码
In [12]label_set=set()for label in tqdm(train_label): label_set.add(label)登录后复制100%|██████████| 752471/752471 [00:00<00:00, 2498469.87it/s]登录后复制 In [13]print(label_set)登录后复制{'财经', '科技', '时政', '房产', '社会', '游戏', '家居', '时尚', '股票', 'cai票', '娱乐', '教育', '星座', '体育'}登录后复制 In [14]label_dict=dict()dict_label=dict()for label in label_set: label_dict[label]=len(label_dict) dict_label[len(label_dict)-1]=label登录后复制 In [15]print(label_dict)print(dict_label)登录后复制{'财经': 0, '科技': 1, '时政': 2, '房产': 3, '社会': 4, '游戏': 5, '家居': 6, '时尚': 7, '股票': 8, 'cai票': 9, '娱乐': 10, '教育': 11, '星座': 12, '体育': 13}{0: '财经', 1: '科技', 2: '时政', 3: '房产', 4: '社会', 5: '游戏', 6: '家居', 7: '时尚', 8: '股票', 9: 'cai票', 10: '娱乐', 11: '教育', 12: '星座', 13: '体育'}登录后复制6.统计标题的长度分布
目的是确定我们网络的输入长度,由统计结果可以看出,绝大部分的标题分词后长度都在20以内,因此我们可以将网络是最大输入长度设为20.(亦可以设为实际的最大长度,虽然这样考虑到了所有的输入,但是没必要,因为很多输入会过于稀疏)
In [16]alllen_dict=dict()for data in train_data: length=len(data) if length not in alllen_dict: alllen_dict[length]=0 alllen_dict[length]+=1登录后复制 In [17]alllen_dict = sorted(alllen_dict.items(), key = lambda x:x[0], reverse = False)print(alllen_dict)登录后复制[(1, 25), (2, 225), (3, 941), (4, 4629), (5, 17045), (6, 36478), (7, 58085), (8, 80255), (9, 99215), (10, 106161), (11, 98791), (12, 88984), (13, 71851), (14, 47479), (15, 25321), (16, 10877), (17, 4111), (18, 1401), (19, 408), (20, 139), (21, 38), (22, 11), (24, 1)]登录后复制 In [18]x=[l[0] for l in alllen_dict]y=[l[1] for l in alllen_dict]plt.bar(x, y) plt.xlabel('length')plt.ylabel('nums')plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt.show()登录后复制/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:2349: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working if isinstance(obj, collections.Iterator):/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:2366: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working return list(data) if isinstance(data, collections.MappingView) else dataNo handles with labels found to put in legend.登录后复制登录后复制登录后复制7. 构建词库,并设定词汇频率阈值
7.1 词库
In [19]def build_cropus(data): crpous=[] for i in range(len(data)): crpous.extend(data[i]) return crpous登录后复制 In [20]allcrpous=build_cropus(train_data+val_data+test_data)print(len(allcrpous))登录后复制9404469登录后复制7.2 构造word--->id 和id--->word的映射关系,同时记录每个词汇出现的频率
In [21]# 构造词典,统计每个词的频率,并根据频率将每个词转换为一个整数iddef build_dict(corpus,frequency): # 首先统计每个不同词的频率(出现的次数),使用一个词典记录 word_freq_dict = dict() for word in corpus: if word not in word_freq_dict: word_freq_dict[word] = 0 word_freq_dict[word] += 1 # 将这个词典中的词,按照出现次数排序,出现次数越高,排序越靠前 word_freq_dict = sorted(word_freq_dict.items(), key = lambda x:x[1], reverse = True) # 构造3个不同的词典,分别存储, # 每个词到id的映射关系:word2id_dict # 每个id到词的映射关系:id2word_dict word2id_dict = {'登录后复制 In [22]':0,' ':1} id2word_dict = {0:' ',1:' '} # 按照频率,从高到低,开始遍历每个单词,并为这个单词构造一个独一无二的id for word, freq in word_freq_dict: if freq>frequency: curr_id = len(word2id_dict) word2id_dict[word] = curr_id id2word_dict[curr_id] = word else: word2id_dict[word]=1 return word2id_dict, id2word_dict,word_freq_dict word_fre=1word2id_dict,id2word_dict,word_counts=build_dict(allcrpous,word_fre)print(len(word2id_dict))print(len(id2word_dict))登录后复制267684149017登录后复制 In [23]vocab_maxlen=len(word2id_dict)print('有',len(word2id_dict),'个字被映射到',len(id2word_dict),'个id上') # 字:id登录后复制有 267684 个字被映射到 149017 个id上登录后复制7.3 根据每个词汇出现的频率统计 每个频率出现的次数;进而限定词汇频率阈值
In [24]counts_word_dict=dict()for word,counts in word_counts: if counts not in counts_word_dict: counts_word_dict[counts]=0 counts_word_dict[counts]+=1counts_word_dict = sorted(counts_word_dict.items(), key = lambda x:x[0], reverse = False)#print(counts_word_dict)x=[l[0] for l in counts_word_dict]y=[l[1] for l in counts_word_dict]plt.bar(x[:10], y[:10]) plt.xlabel('frequency')plt.ylabel('nums')plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt.show()登录后复制No handles with labels found to put in legend.登录后复制登录后复制登录后复制7.4 总共的词汇有26万7千个,而仅出现1次的词汇就占了12万个,我们可以认为仅出现1次的词汇是无关紧要的。 根据这个结果,确定word_freq=1,之后也可进行实验验证其他长度是否更优。
8.根据word2id_dict将标题文本和标签向量化
In [25]tensor_maxlen=15 # 根据统计到的标题长度分布设定vocab_size=len(id2word_dict) # 词汇量登录后复制 In [26]def build_tensor(data,dicta,maxlen): tensor=[] for i in range(len(data)): subtensor=[] lista=data[i] for j in range(len(lista)): index=dicta.get(lista[j]) subtensor.append(index) # 长度限定,不足补0 ;超过则截断 if len(subtensor) < maxlen: subtensor+=[0]*(maxlen-len(subtensor)) else: subtensor=subtensor[:maxlen] tensor.append(subtensor) return tensor登录后复制 In [27]train_tensor=paddle.to_tensor(np.array(build_tensor(train_data,word2id_dict,tensor_maxlen)))val_tensor=paddle.to_tensor(np.array(build_tensor(val_data,word2id_dict,tensor_maxlen)))test_tensor=np.array(build_tensor(test_data,word2id_dict,tensor_maxlen))登录后复制 In [28]print(train_tensor.shape)print(train_tensor[0])print(type(train_tensor))print(val_tensor.shape)print(val_tensor[0])print(type(val_tensor))print(test_tensor.shape)print(test_tensor[0])print(type(test_tensor))登录后复制[752471, 15]登录后复制W1222 21:06:31.478082 1304 device_context.cc:447] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 7.0, Driver API Version: 10.1, Runtime API Version: 10.1W1222 21:06:31.482895 1304 device_context.cc:465] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.登录后复制Tensor(shape=[15], dtype=int64, place=CUDAPlace(0), stop_gradient=True, [2739, 2054, 216 , 2193, 1240, 121 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ])登录后复制[80000, 15]Tensor(shape=[15], dtype=int64, place=CUDAPlace(0), stop_gradient=True, [1580, 1539, 677 , 3582, 4690, 42 , 6238, 75 , 41 , 69 , 3930, 32 , 9496, 0 , 0 ]) (83599, 15)[ 60 59529 4269 9297 69435 2 6721 572 2403 1 16 0 0 0 0] #将token出现的频率保存到文件中。
with open('./data/word_counts.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') as word: for i in word_counts: word.write(str(i)+'\n')
到这里,data部分的向量化完成,下面进行label的向量化
In [29]print(train_label[0])print(val_label[0])print(label_dict)def get_label_tensor(dict,label): tensor=[] for d in label: tensor.append(dict[d]) return tensor# def test_lable_tensor(lena):# tensor=[]# for i in range(lena):# tensor.append(0)# return tensor登录后复制科技cai票{'财经': 0, '科技': 1, '时政': 2, '房产': 3, '社会': 4, '游戏': 5, '家居': 6, '时尚': 7, '股票': 8, 'cai票': 9, '娱乐': 10, '教育': 11, '星座': 12, '体育': 13}登录后复制 In [30]train_label_tensor=np.array(get_label_tensor(label_dict,train_label))val_label_tensor=np.array(get_label_tensor(label_dict,val_label))# test_lable_tensor=np.array(test_label_tesnor(len(test_tensor)))登录后复制 In [31]print(train_label_tensor[0])登录后复制1登录后复制 In [32]numclass=len(label_set)train_label_tensor=paddle.to_tensor(train_label_tensor,dtype='int64')val_label_tensor=paddle.to_tensor(val_label_tensor,dtype='int64')# test_label_tensor=paddle.to_tensor(test_label_tensor,dtype='int64')# train_label_tensor=paddle.nn.functional.one_hot(paddle.to_tensor(train_label_tensor,dtype='int32'),numclass)# val_label_tensor=paddle.nn.functional.one_hot(paddle.to_tensor(val_label_tensor,dtype='int32'),numclass)登录后复制 In [33]print(type(train_label_tensor))print(train_label_tensor[0])print(train_label_tensor.shape)print(val_label_tensor.shape)# print(test_label_tensor.shape)登录后复制登录后复制Tensor(shape=[1], dtype=int64, place=CUDAPlace(0), stop_gradient=True, [1])[752471][80000] 9.搭建网络
9.1创建数据集
In [34]class MyDataset(paddle.io.Dataset): """ 步骤一:继承paddle.io.Dataset类 """ def __init__(self, title,lable): """ 步骤二:实现构造函数,定义数据集大小 """ super(MyDataset, self).__init__() self.title = title self.lable=lable def __getitem__(self, index): """ 步骤三:实现__getitem__方法,定义指定index时如何获取数据,并返回单条数据(训练数据,对应的标签) """ # if self.lable==None: # return self.title[index] # else: return self.title[index], self.lable[index] def __len__(self): """ 步骤四:实现__len__方法,返回数据集总数目 """ return self.title.shape[0]登录后复制 In [35]BATCH_SIZE=128embed_dim=256hidden_size=128train_batch_num=train_tensor.shape[0]//BATCH_SIZE #3482val_batch_num=val_tensor.shape[0]//BATCH_SIZE #156print(train_batch_num)print(val_batch_num)登录后复制5878625登录后复制 In [36]# 定义数据集train_dataset = MyDataset(train_tensor,train_label_tensor)train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True,drop_last=True)val_dataset=MyDataset(val_tensor,val_label_tensor)val_loader=paddle.io.DataLoader(val_dataset,batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,shuffle=True,drop_last=True)# test_dataset=MyDataset(test_tensor,train_label_tensor)# test_loader=paddle.io.DataLoader(val_dataset,batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)登录后复制j=0 for i in train_loader: print(len(i)) for ind,each in enumerate(i): #print(ind,each.shape,each) print(ind,each) j+=1 if j==2: break
9.2 使用Embedding+GRU+MLP进行分类
GRU的内部结构如下,但是我们在使用的时候只需要一行代码即可。
In [37]
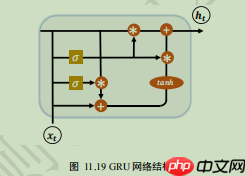 class Mynet(paddle.nn.Layer): def __init__(self,vocab_size,embed_dim,hidden_size,data_maxlen,numclass): super(Mynet,self).__init__() self.numclass=numclass self.data_maxlen=data_maxlen self.vocab_size=vocab_size self.embed_dim=embed_dim self.emb=paddle.nn.Embedding(vocab_size,embed_dim) self.gru=paddle.nn.GRU(embed_dim,hidden_size,2) self.l1=paddle.nn.Linear(hidden_size,64) self.l2=paddle.nn.Linear(64,32) self.l3=paddle.nn.Linear(32,self.numclass) self.drop=paddle.nn.Dropout(0.5) def forward(self,x): x=self.emb(x) x,states=self.gru(x) x=paddle.mean(x,axis=1) x=self.drop(x) out=paddle.nn.functional.relu(self.l1(x)) out=self.drop(out) out=paddle.nn.functional.relu(self.l2(out)) out=self.l3(out) out=paddle.nn.functional.softmax(out,axis=-1) return out登录后复制 In [38]mynet=Mynet(vocab_size,embed_dim,hidden_size,tensor_maxlen,numclass)登录后复制 In [39]paddle.summary(mynet,(128,15),dtypes='int64')登录后复制-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Layer (type) Input Shape Output Shape Param # ====================================================================================== Embedding-1 [[128, 15]] [128, 15, 256] 38,148,352 GRU-1 [[128, 15, 256]] [[128, 15, 128], [2, 128, 128]] 247,296 Dropout-1 [[128, 64]] [128, 64] 0 Linear-1 [[128, 128]] [128, 64] 8,256 Linear-2 [[128, 64]] [128, 32] 2,080 Linear-3 [[128, 32]] [128, 14] 462 ======================================================================================Total params: 38,406,446Trainable params: 38,406,446Non-trainable params: 0--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Input size (MB): 0.01Forward/backward pass size (MB): 6.04Params size (MB): 146.51Estimated Total Size (MB): 152.56--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------登录后复制
class Mynet(paddle.nn.Layer): def __init__(self,vocab_size,embed_dim,hidden_size,data_maxlen,numclass): super(Mynet,self).__init__() self.numclass=numclass self.data_maxlen=data_maxlen self.vocab_size=vocab_size self.embed_dim=embed_dim self.emb=paddle.nn.Embedding(vocab_size,embed_dim) self.gru=paddle.nn.GRU(embed_dim,hidden_size,2) self.l1=paddle.nn.Linear(hidden_size,64) self.l2=paddle.nn.Linear(64,32) self.l3=paddle.nn.Linear(32,self.numclass) self.drop=paddle.nn.Dropout(0.5) def forward(self,x): x=self.emb(x) x,states=self.gru(x) x=paddle.mean(x,axis=1) x=self.drop(x) out=paddle.nn.functional.relu(self.l1(x)) out=self.drop(out) out=paddle.nn.functional.relu(self.l2(out)) out=self.l3(out) out=paddle.nn.functional.softmax(out,axis=-1) return out登录后复制 In [38]mynet=Mynet(vocab_size,embed_dim,hidden_size,tensor_maxlen,numclass)登录后复制 In [39]paddle.summary(mynet,(128,15),dtypes='int64')登录后复制-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Layer (type) Input Shape Output Shape Param # ====================================================================================== Embedding-1 [[128, 15]] [128, 15, 256] 38,148,352 GRU-1 [[128, 15, 256]] [[128, 15, 128], [2, 128, 128]] 247,296 Dropout-1 [[128, 64]] [128, 64] 0 Linear-1 [[128, 128]] [128, 64] 8,256 Linear-2 [[128, 64]] [128, 32] 2,080 Linear-3 [[128, 32]] [128, 14] 462 ======================================================================================Total params: 38,406,446Trainable params: 38,406,446Non-trainable params: 0--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Input size (MB): 0.01Forward/backward pass size (MB): 6.04Params size (MB): 146.51Estimated Total Size (MB): 152.56--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------登录后复制{'total_params': 38406446, 'trainable_params': 38406446}登录后复制 In [40]epochs = 20lr=0.001log_freq=1000model_path='./model/train_model'登录后复制9.3训练网络
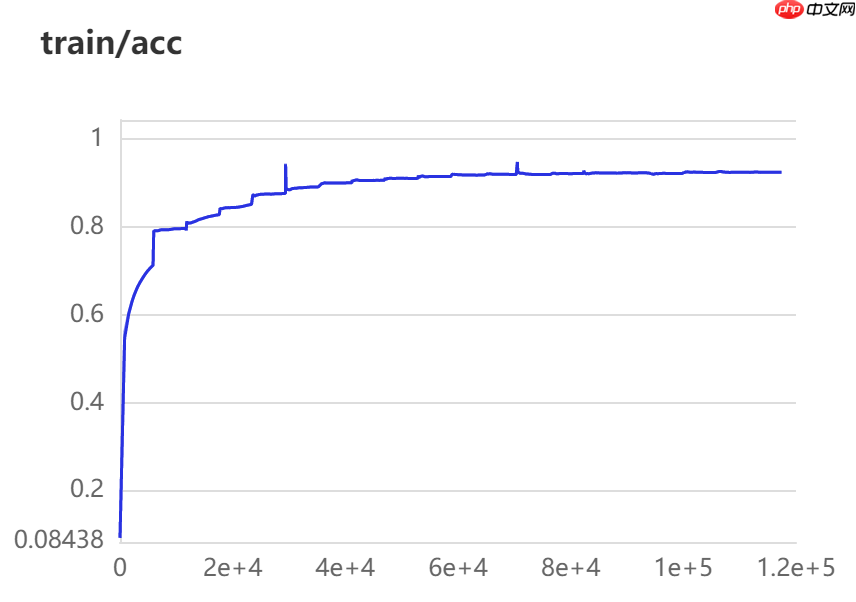
In [41]model=paddle.Model(mynet)# 为模型训练做准备,设置优化器,损失函数和精度计算方式model.prepare(optimizer=paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=lr,parameters=model.parameters()), loss=paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(), metrics=paddle.metric.Accuracy())登录后复制 In [ ]model.fit(train_data=train_loader, eval_data=val_loader, epochs=epochs, eval_freq=1, save_freq=5, save_dir=model_path, verbose=1, callbacks=[paddle.callbacks.VisualDL('./log')])登录后复制9.4 训练精度展示 20epochs:
In [43]

model.save('./model/infer')登录后复制10.加载网络进行预测
10.1 加载训练好的模型
In [44]infer_model=paddle.Model(Mynet(vocab_size,embed_dim,hidden_size,tensor_maxlen,numclass))infer_model.load('./model/infer')登录后复制 In [45]with open('result.txt','w',encoding="utf-8") as res: for title in test_tensor: re = infer_model.predict_batch([[title]]) #print(re) index=paddle.argmax(paddle.to_tensor(re)) index=int(index[0]) #print(type(index)) #print(dict_label[index]) res.write(dict_label[index]+'\n')print('_____________over__________over______________')登录后复制/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle/tensor/creation.py:130: DeprecationWarning: `np.object` is a deprecated alias for the builtin `object`. To silence this warning, use `object` by itself. Doing this will not modify any behavior and is safe. Deprecated in NumPy 1.20; for more details and guidance: https://numpy.org/devdocs/release/1.20.0-notes.html#deprecations if data.dtype == np.object:登录后复制_____________over__________over______________登录后复制
免责声明
游乐网为非赢利性网站,所展示的游戏/软件/文章内容均来自于互联网或第三方用户上传分享,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系youleyoucom@outlook.com。
同类文章
AI驱动存储芯片市场爆发,2027年或达3000亿规模
全球存储芯片市场正经历一场由人工智能(AI)需求主导的深刻变革。摩根大通分析师团队在最新报告中指出,云服务提供商对高性能内存的旺盛需求,正推动整个行业进入长期结构性增长通道。这场变革不仅重塑了DRA
真我GT8 Pro首发2K 144Hz京东方直屏
9月26日消息,真我realme官方正式宣布,真我GT8 Pro将联合京东方全球首发2K 144Hz“苍穹屏”,官方将其定位为“神级
OPPO Find X9首发4K实况照片 影像体验再升级
9月26日消息,OPPO宣布其全新Find X9系列手机将全球首发“直出4K超清实况照片”功能,这一创新技术标志着手机影像领域的一次
vivo X300系列重构移动影像体验,全链路创新开启场景化创作新时代
9月26日,vivo在“X系列蓝图影像技术沟通会”上揭晓全新影像战略,宣布以“场景解决方案”为核心构建开放生态,推动移动影像从工具属
OPPO Find X9红色限定版亮相,绒砂工艺重塑高端质感
9月26日消息,OPPO官方微博发布了全新的产品外观图,其中Find X9系列红色特别版首次亮相。这款采用全新红色设计的旗舰新机,以
相关攻略
热门教程
更多- 游戏攻略
- 安卓教程
- 苹果教程
- 电脑教程